Connecting Continents: Advances in Logistics
Modern logistics systems have transformed how goods and people move across the globe. From sophisticated tracking technologies to multimodal transport networks, the infrastructure connecting continents continues to evolve rapidly. Understanding these advancements helps businesses and travelers navigate an increasingly interconnected world where efficiency, sustainability, and reliability define success in global movement.
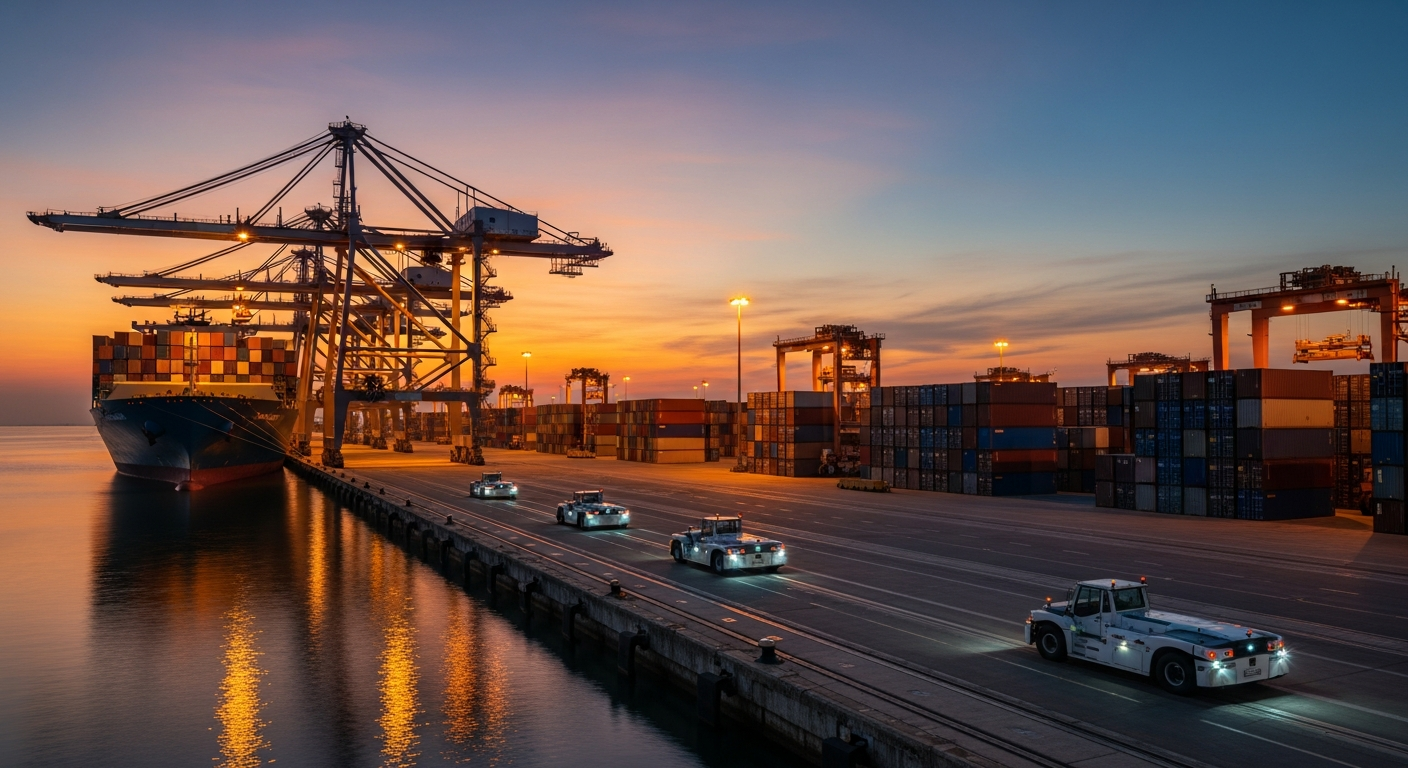

The global logistics industry has undergone remarkable transformation in recent decades, reshaping how continents connect and interact. Advanced technologies, innovative infrastructure, and strategic planning have created seamless pathways for goods, services, and people to traverse vast distances with unprecedented efficiency.
How Does Modern Journey Planning Enhance Global Connectivity?
Contemporary journey planning leverages sophisticated algorithms and real-time data to optimize routes across multiple continents. Digital platforms now integrate various transportation modes, allowing seamless transitions between air, sea, rail, and road networks. GPS technology and satellite communications enable precise tracking throughout the entire voyage, providing transparency and accountability. Travelers and logistics managers can monitor progress, anticipate delays, and adjust plans dynamically. These systems reduce uncertainty and improve resource allocation, making international movement more predictable and cost-effective than ever before.
What Role Does Transit Infrastructure Play in Continental Connections?
Transit hubs serve as critical nodes in the global logistics network, facilitating the transfer of cargo and passengers between different transportation systems. Major ports, airports, and rail terminals have invested heavily in automation and capacity expansion to handle increasing volumes. Intermodal facilities enable containers to move smoothly from ships to trains or trucks without unpacking, reducing handling time and costs. Strategic location of these hubs near economic centers and along major trade routes maximizes efficiency. Investment in transit infrastructure directly correlates with regional economic growth and competitiveness in the global marketplace.
How Have Logistics Technologies Transformed Global Movement?
Technological innovation has revolutionized logistics operations across continents. Blockchain systems provide secure, transparent records of shipments throughout their journey, reducing fraud and disputes. Artificial intelligence optimizes warehouse operations, predicting demand patterns and streamlining inventory management. Autonomous vehicles and drones are beginning to handle last-mile delivery in urban areas, addressing congestion and labor challenges. Internet of Things sensors monitor cargo conditions in real-time, ensuring temperature-sensitive goods maintain quality during transit. These technologies collectively enhance reliability, reduce waste, and lower operational costs across the supply chain.
What Factors Influence Mobility Across International Routes?
Several elements determine the efficiency and accessibility of international mobility. Regulatory frameworks, including customs procedures and visa requirements, significantly impact movement speed. Trade agreements between nations can streamline border crossings and reduce administrative burdens. Infrastructure quality varies considerably between regions, affecting transit times and costs. Geopolitical stability influences route selection, as logistics providers seek to minimize risk. Environmental considerations increasingly shape routing decisions, with companies balancing speed against carbon footprint. Understanding these factors helps organizations develop resilient strategies for global operations.
How Do Different Pathways Connect Global Destinations?
Multiple transportation corridors link continents, each offering distinct advantages. Maritime routes handle the majority of global cargo volume, with container ships traversing established sea lanes between major ports. Air freight provides speed for time-sensitive or high-value goods, connecting distant destinations within hours. Rail networks, particularly in Eurasia, offer middle-ground solutions between cost and speed. Road transport dominates last-mile delivery and regional distribution. Increasingly, companies employ multimodal strategies, combining these pathways to optimize cost, speed, and reliability based on specific cargo requirements and destination characteristics.
What Does Global Logistics Cost in Today’s Market?
Logistics expenses vary significantly based on distance, mode, cargo type, and service level. Understanding typical cost structures helps businesses budget effectively for international operations. The following table provides general cost estimations for common logistics services:
| Service Type | Provider Examples | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Ocean Freight (Container) | Maersk, MSC, CMA CGM | $1,500-$4,000 per 20ft container |
| Air Freight | FedEx, DHL, UPS | $3-$8 per kilogram |
| Rail Freight (International) | DB Cargo, BNSF, China Railway | $500-$2,000 per container |
| Road Freight (Long Distance) | Schneider, J.B. Hunt, XPO | $1.50-$3.00 per mile |
| Express Courier | TNT, Aramex, SF Express | $20-$100 per package |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Actual costs depend on numerous variables including fuel prices, seasonal demand, route congestion, and contract negotiations. Many providers offer volume discounts and long-term agreements that can significantly reduce per-unit expenses. Additional fees for customs clearance, insurance, and special handling may apply. Businesses should request detailed quotes and compare multiple providers to optimize their logistics spending.
How Does Exploration of New Routes Impact Global Commerce?
The continuous exploration and development of new transportation routes reshape global trade patterns. Arctic shipping lanes, made accessible by climate change, offer shorter distances between Asia and Europe, potentially reducing transit times by days. New rail corridors through Central Asia provide alternatives to traditional maritime routes, enhancing connectivity for landlocked regions. Investment in port infrastructure in developing regions opens previously underserved markets to international commerce. These emerging pathways create competitive pressure on established routes, driving innovation and efficiency improvements across the entire logistics sector. Companies that adapt quickly to these changes gain strategic advantages in serving global markets.
What Defines the Modern Traveler Experience in Global Transit?
Today’s international traveler benefits from integrated systems that simplify complex journeys across multiple continents. Digital ticketing platforms consolidate bookings across airlines, trains, and ground transportation. Mobile applications provide real-time updates, gate changes, and alternative routing options during disruptions. Biometric identification systems expedite security and immigration processes at major hubs. Loyalty programs increasingly partner across transportation modes, offering seamless benefits regardless of journey segment. Enhanced connectivity through Wi-Fi and cellular networks keeps travelers productive during transit. These improvements reflect broader trends in logistics, where customer experience and operational efficiency advance together.
The advances connecting continents through improved logistics represent more than technological achievement. They reflect evolving global relationships, economic interdependence, and shared commitment to efficient resource use. As systems continue to mature, the distinction between local and global commerce diminishes, creating opportunities for businesses and individuals worldwide. Understanding these developments positions organizations to leverage global networks effectively while navigating the complexities of international movement in an interconnected world.