Sustainable Transport Technologies
The global landscape of transportation is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by a pressing need for environmental stewardship and enhanced efficiency. Innovations in sustainable transport technologies are reshaping how people and goods move, offering solutions that aim to reduce carbon footprints, mitigate air pollution, and conserve natural resources. This evolving sector encompasses a wide array of advancements, from electrified powertrains to intelligent infrastructure, all contributing to a more resilient and environmentally conscious future for mobility worldwide.

The Evolution of Electric Vehicles and Mobility
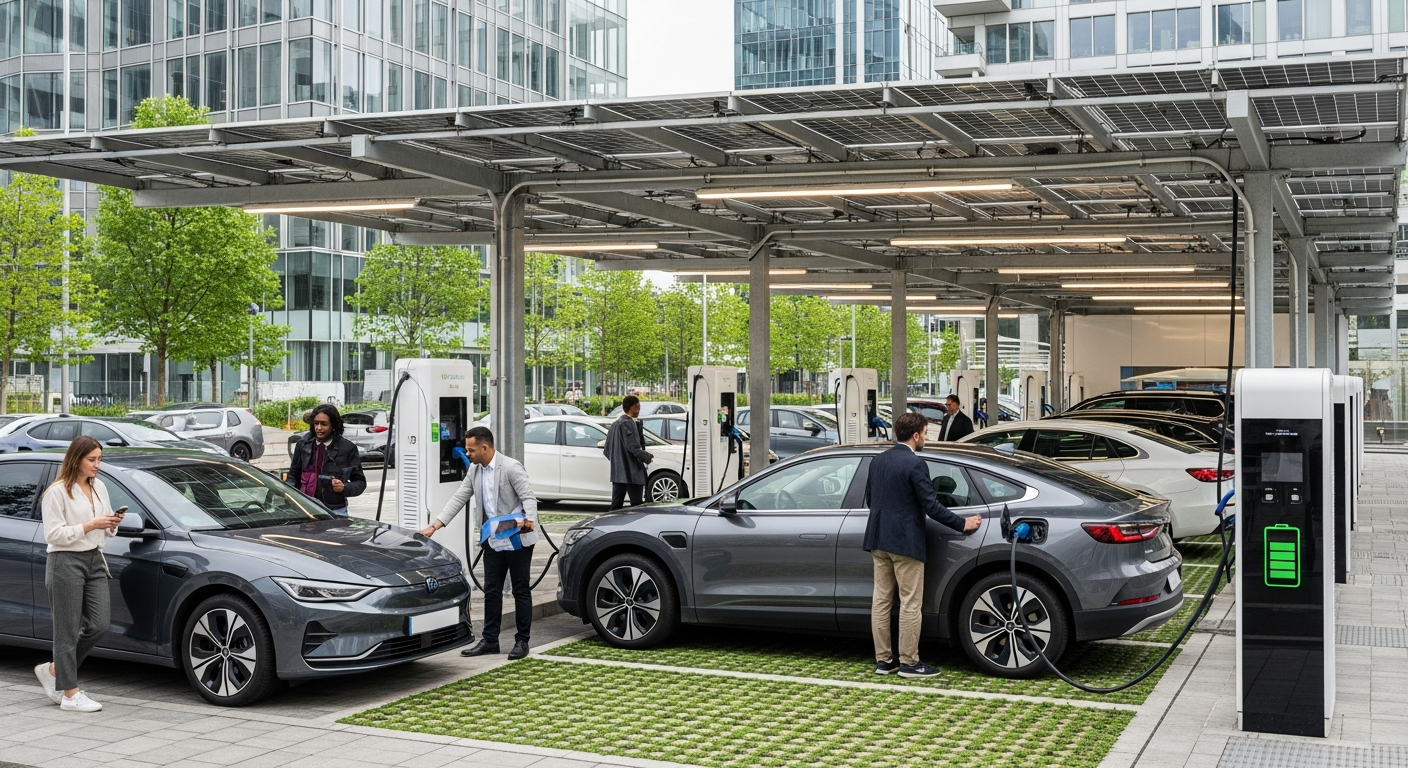
The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) represents a cornerstone of sustainable mobility. Modern automotive engineering has advanced significantly, moving beyond traditional internal combustion engines to embrace electric motors. These vehicles, including battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), offer reduced tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air in urban environments. The continuous innovation in battery technology is leading to increased range, faster charging times, and greater performance, making electric cars a viable and increasingly popular choice for many drivers. Beyond personal vehicles, electric solutions are also being integrated into public transport systems, such as electric buses and trains, further enhancing sustainable transport networks.
Advancements in Autonomous Driving and Road Safety
Autonomous driving technology is poised to revolutionize transport, promising not only greater convenience but also significant improvements in road safety and efficiency. These vehicles, equipped with sophisticated sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence, are designed to perceive their environment and operate without human intervention. The development of autonomous systems has a direct impact on reducing human error, which is a major contributor to accidents. Furthermore, autonomous vehicles can optimize routes and driving patterns, leading to smoother traffic flow and potentially lower energy consumption. The integration of these advanced technologies into future transport systems requires robust engineering and careful consideration of safety protocols and infrastructure modifications.
Materials, Design, and Efficiency in Modern Automotive Engineering
Sustainable transport extends beyond the powertrain to encompass the very materials and design principles used in vehicle manufacturing. Automotive engineering is increasingly focused on lightweight materials, such as advanced composites and aluminum alloys, to reduce vehicle mass and improve fuel efficiency or electric range. Aerodynamic design plays a crucial role in minimizing drag, further enhancing efficiency across all types of vehicles. The entire lifecycle of a vehicle, from production to recycling, is being scrutinized to minimize environmental impact. This includes exploring sustainable materials, optimizing manufacturing processes, and designing components for easier disassembly and reuse, aligning with principles of a circular economy.
Exploring Alternative Fuels and Future Transport Solutions
While electric power is a prominent solution, the future of sustainable transport also involves a diverse portfolio of alternative fuels and innovative technologies. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, for instance, offer another pathway to zero-emission driving, producing only water vapor as a byproduct. Biofuels, derived from renewable biomass sources, can offer a lower-carbon alternative for certain transport sectors, particularly in aviation and heavy-duty vehicles, where electrification faces greater challenges. Furthermore, advancements in smart infrastructure, such as vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication and intelligent traffic management systems, are crucial for optimizing overall transport efficiency and reducing congestion on roads, contributing to a more sustainable and integrated mobility experience.
Economic Aspects of Sustainable Transport Adoption
Adopting sustainable transport technologies often involves an initial investment, which can vary significantly depending on the chosen solution. For electric vehicles, the purchase price can sometimes be higher than comparable gasoline cars, though this gap is narrowing. However, operating costs, including fuel (electricity) and maintenance, are typically lower. Public transport initiatives, such as electric bus fleets or expanded rail networks, require substantial government or private sector funding but offer long-term benefits in reduced congestion, pollution, and improved urban mobility. Micromobility options, like electric scooters and bikes, generally have lower entry costs and operating expenses, making them accessible alternatives for short-distance travel in urban areas.
| Sustainable Transport Type | Key Benefits | Estimated Adoption Cost (Initial/Operating) |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Zero emissions, lower running costs, quiet operation | Moderate to High (Initial), Low (Operating) |
| Public Transport (Electric Buses/Trains) | Reduced individual vehicle use, lower collective emissions, urban decongestion | High (Infrastructure), Low (User Fares) |
| Micromobility (E-bikes, E-scooters) | Low emissions, convenient for short distances, reduced traffic | Low to Moderate (Initial), Low (Operating) |
| Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles | Zero emissions, fast refueling, longer range | High (Initial), Moderate (Operating) |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Mobility
The trajectory of sustainable transport technologies points towards continued innovation and integration. The ongoing research and development in areas like battery chemistry, advanced materials, and artificial intelligence will further refine existing solutions and unlock new possibilities. The convergence of electric, autonomous, and connected technologies promises a future where transport is not only environmentally friendly but also safer, more efficient, and more accessible. Addressing the challenges of infrastructure development, policy support, and consumer adoption will be key to realizing the full potential of these transformative advancements in mobility worldwide.