Vehicle Aerodynamics and Fuel Efficiency
Understanding how air interacts with a moving vehicle is crucial for optimizing its performance and minimizing fuel consumption. Vehicle aerodynamics, a specialized field within automotive engineering, focuses on designing cars and other transport methods to reduce air resistance. This reduction not only contributes to better fuel efficiency but also enhances stability and handling, making it a cornerstone of modern automotive design and a key factor in the ongoing pursuit of sustainable mobility.
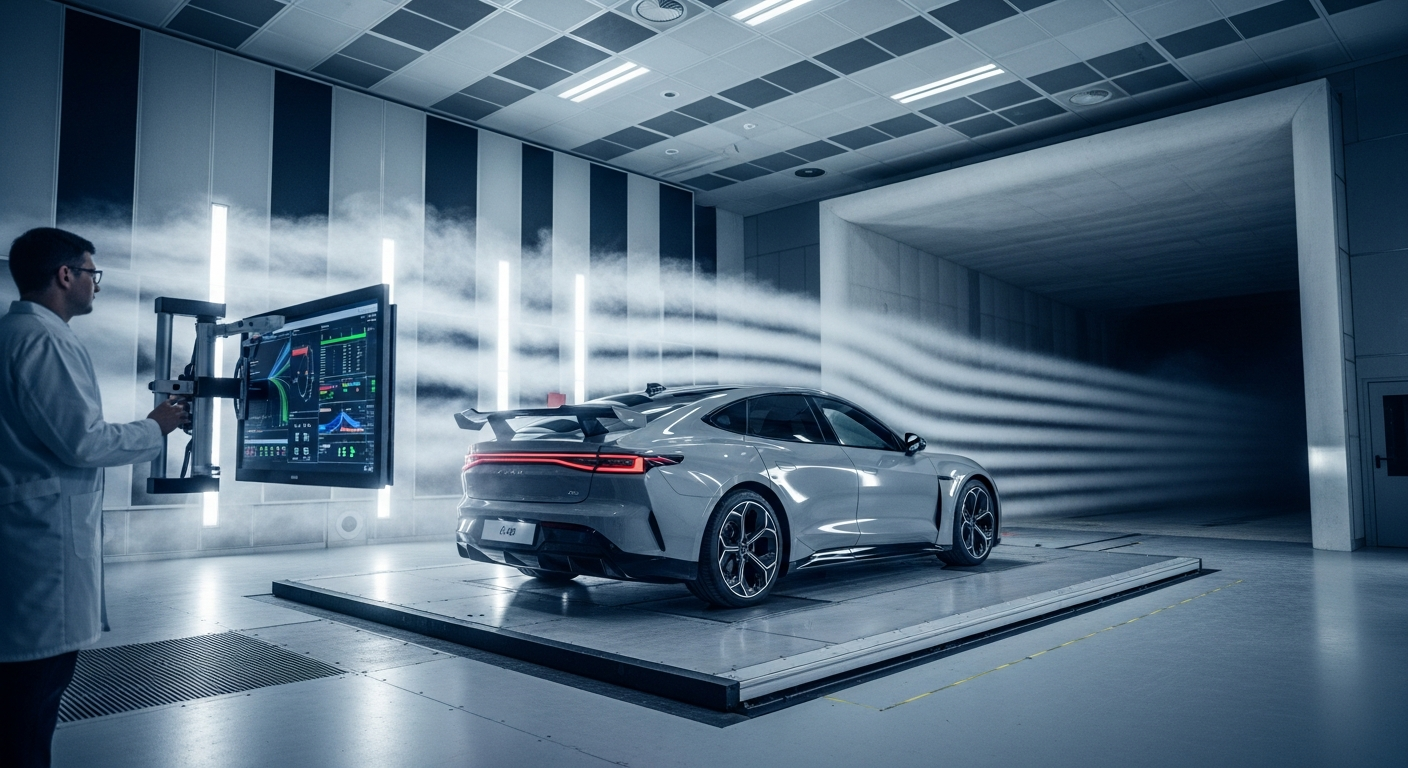

Understanding Automotive Aerodynamics Principles
Automotive aerodynamics is the study of how air flows around a moving vehicle and the forces it exerts. The primary force of concern is drag, which opposes a vehicle’s motion. Other forces include lift, which can reduce tire grip, and downforce, which can increase it. Minimizing aerodynamic drag is a critical objective in vehicle design, as overcoming this resistance accounts for a significant portion of a vehicle’s energy consumption, especially at higher speeds. Engineers utilize principles of fluid dynamics to sculpt vehicle bodies, aiming for smooth airflow and reduced turbulence, which directly translates to less energy required from the engine to maintain speed.
Design Elements for Enhanced Vehicle Efficiency
Modern vehicle design incorporates numerous elements to improve aerodynamic efficiency. Streamlined body shapes, such as teardrop profiles, are fundamental. Beyond the overall shape, specific features play a vital role. Underbody panels create a smoother surface beneath the car, reducing turbulence. Spoilers and diffusers are not just aesthetic additions; they manage airflow at the rear of the vehicle, reducing drag and sometimes generating beneficial downforce. Active grille shutters, which open and close based on cooling needs, are another technological advancement that optimizes airflow through the engine bay, further contributing to the vehicle’s overall aerodynamic performance and fuel efficiency.
Impact on Fuel Consumption and Sustainability
The direct correlation between reduced aerodynamic drag and improved fuel consumption is substantial. For conventional internal combustion engine vehicles, less drag means the engine has to work less to overcome air resistance, leading to lower fuel usage and, consequently, reduced emissions. This contributes significantly to environmental sustainability. For electric and hybrid vehicles, enhanced aerodynamics extends their driving range by minimizing the energy drain from the battery. As the automotive industry continues to prioritize efficiency and environmental responsibility, aerodynamic optimization remains a key strategy across all types of vehicles.
Aerodynamics in Modern Vehicle Manufacturing
In the manufacturing process of modern vehicles, advanced technology plays a pivotal role in aerodynamic development. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software allows engineers to simulate airflow around virtual vehicle models, identifying areas for improvement without physical prototypes. Wind tunnel testing, a long-standing practice, complements CFD by providing real-world data on drag, lift, and other aerodynamic forces. This iterative design and testing process ensures that new cars are as aerodynamically efficient as possible before they reach production, reflecting a continuous commitment to innovation in automotive technology.
Future Trends in Vehicle Aerodynamic Design
The future of vehicle aerodynamics is characterized by ongoing innovation and adaptation to new mobility paradigms. Active aerodynamics, which involves movable components like adjustable spoilers or ride height systems that adapt to driving conditions, is becoming more prevalent. These systems can dynamically optimize airflow for different speeds or driving scenarios. The rise of electric vehicles also drives new aerodynamic considerations, as their powertrains often allow for more radical body designs. Furthermore, the development of autonomous vehicles may lead to new forms and functions that prioritize aerodynamic efficiency in novel ways, shaping the future of transport and driving experiences.
Conclusion
Vehicle aerodynamics is an indispensable aspect of automotive engineering, profoundly influencing fuel efficiency, stability, and overall driving dynamics. Through continuous advancements in design, technology, and manufacturing processes, engineers consistently strive to minimize air resistance. This focus not only helps reduce fuel consumption and emissions but also extends the range of electric vehicles, contributing to a more sustainable and efficient future for all forms of mobility and transport.